Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets. Earth formed approximately 4.54 billion years ago, and life appeared on its surface within its first billion years. Earth's biosphere then significantly altered the atmospheric and other basic physical conditions, which enabled the proliferation of organisms as well as the formation of the ozone layer, which together with Earth's magnetic field blocked harmful solar radiation, and permitted formerly ocean-confined life to move safely to land. The physical properties of the Earth, as well as its geological history and orbit, have allowed life to persist.
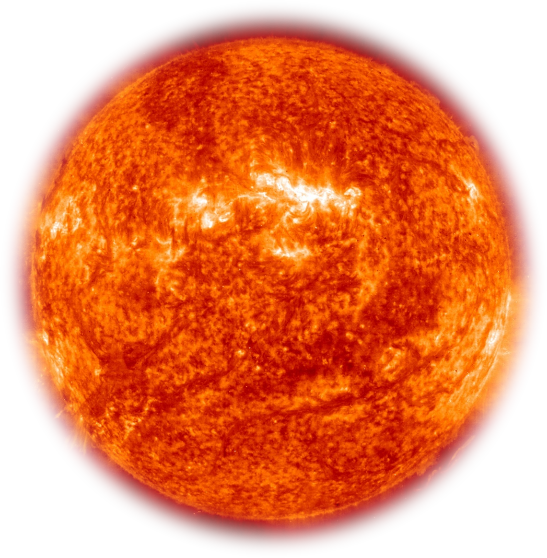
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is almost perfectly spherical and consists of hot plasma interwoven with magnetic fields.It has a diameter of about 1,392,684 km (865,374 mi),around 109 times that of Earth, and its mass (1.989×1030 kilograms, approximately 330,000 times the mass of Earth) accounts for about 99.86% of the total mass of the Solar System. Chemically, about three quarters of the Sun's mass consists of hydrogen, while the rest is mostly helium. The remainder (1.69%, which nonetheless equals 5,600 times the mass of Earth) consists of heavier elements, including oxygen, carbon, neon and iron, among others.
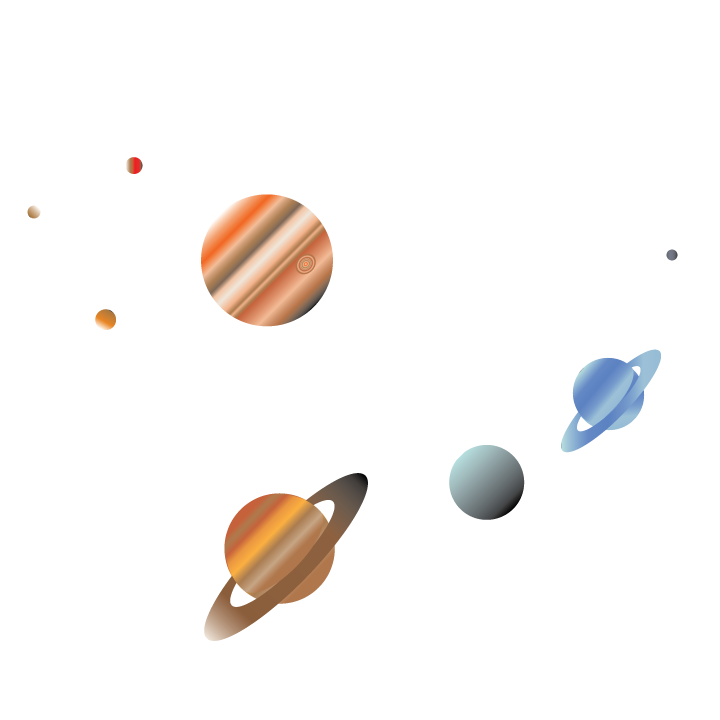
The Solar System comprises the Sun and its planetary system of eight planets, as well as a number of dwarf planets, satellites (moons), and other objects that orbit the Sun. It formed 4.6 billion years ago from the gravitational collapse of a giant molecular cloud. The vast majority of the system's mass is in the Sun, with most of the remaining mass contained in Jupiter. The four smaller inner planets, Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars, also called the terrestrial planets, are primarily composed of rock and metal. The four outer planets, called the gas giants, are substantially more massive than the terrestrials. The two largest, Jupiter and Saturn, are composed mainly of hydrogen and helium; the two outermost planets, Uranus and Neptune, are composed largely of substances with relatively high melting points (compared with hydrogen and helium), called ices, such as water, ammonia and methane, and are often referred to separately as "ice giants". All planets have almost circular orbits that lie within a nearly flat disc called the ecliptic plane.
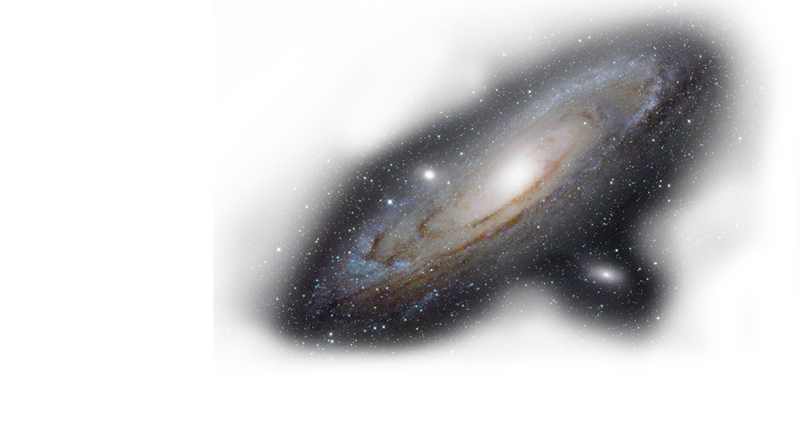
The Milky Way is the galaxy that contains our Solar System.Its name "milky" is derived from its appearance as a dim glowing band arching across the night sky in which the naked eye cannot distinguish individual stars. The term "Milky Way" is a translation of the Classical Latin via lactea, from the Greek γαλαξίας κύκλος ("milky circle"). From the Earth, the Milky Way appears like a band because its disk-shaped structure is viewed from within the Galaxy. Galileo Galilei first resolved the band of light into individual stars with his telescope in 1610. In the past, astronomers thought that all of the stars in the universe were contained inside of the Milky Way. Following the 1920 Great Debate between the astronomers Harlow Shapley and Heber Curtis, observations by Edwin Hubble definitively showed that the Milky Way is just one of many galaxies.
A nebula is an interstellar cloud of dust, hydrogen, helium and other ionized gases. Nebulae are often star-forming regions, such as in the Eagle Nebula. This nebula is depicted in one of NASA's most famous images, the "Pillars of Creation". In these regions the formations of gas, dust, and other materials "clump" together to form larger masses, which attract further matter, and eventually will become massive enough to form stars. The remaining materials are then believed to form planets, and other planetary system objects.